Asian Studies in Business and Economics (ASBE) - Your gateway to the Asian economic region
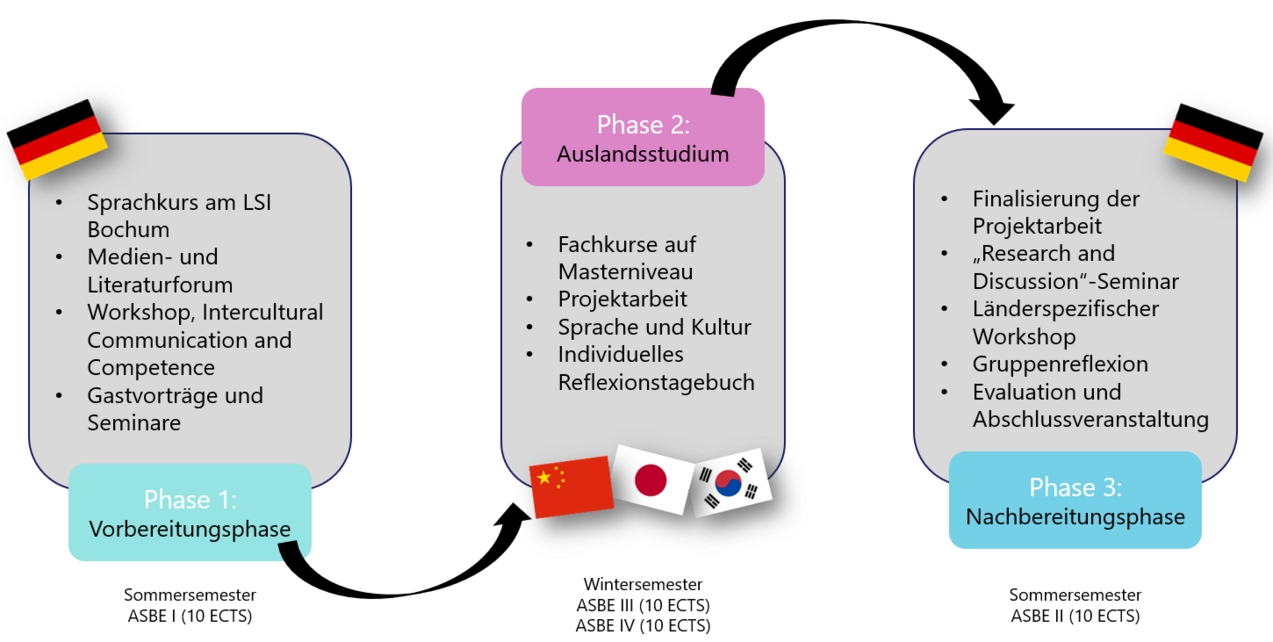
The "Asian Studies in Business and Economics" programme offers Master's students from the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics at Paderborn University the opportunity to take the first step towards an international career. The Asian economic area has experienced enormous growth in recent years and is also becoming increasingly interesting for Europe. The programme is divided into three phases: the preparation phase, the study abroad phase and the follow-up phase.
The contents of the phases can be found here.
Structure of the programme
The "Asian Studies in Business and Economics" programme consists of four container modules of 10 ECTS each. As a rule, the container modules cannot be split up, which is why it is important that you have a total of 4 x 10 ECTS credits open in one of the upper-level areas of your study plan. Completion of the ASBE I - IV modules is compulsory and 40 ECTS credits must be kept free!
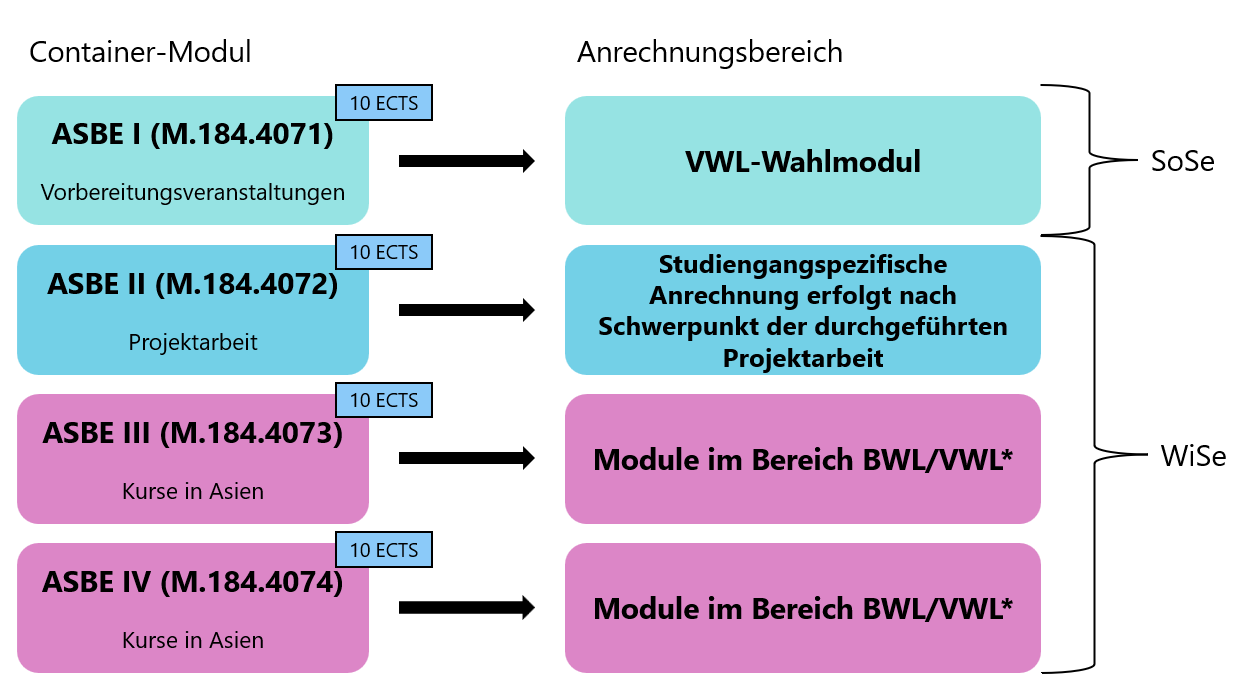
* If your degree programme does not allow full crediting of the courses abroad (20 ECTS) in the field of business administration/economics modules, additional work of at least 10 pages may be required for each container to be credited (ASBE III or IV) in order to ensure that the subject content matches your degree programme specialisation. This regulation does not apply to the field of method modules, which is generally not available as an area for crediting foreign credits.
Preparation phase:
ASBE 1 includes the courses of the preparatory phase and is generally booked in the upper division of Economics/Economics of your study plan. Accordingly, you need 10 ECTS in the field of Economics/Economics that have not yet been taken.
Project work:
ASBE 2 includes the project work. This is booked in the appropriate section of your study plan according to your research topic. Example: If your supervisor is part of the Business Education department, the container module will be booked with 10 ECTS in the upper division of Business Education.
Study abroad:
Depending on the partner university,ASBE 3 and ASBE 4 each consist of 1-2 specialised courses with a total value of 20 ECTS(2x 10 ECTS). Recognition depends on the courses chosen at the partner university.
Contents of the phases
The preparation phase always takes place in the summer semester and consists of two main components. A four-week intensive language course at the Language Institute of the Ruhr University Bochum (LSI) and a course during the semester in which the intercultural competence and Asian expertise of the students is developed.
The intensive language course at the LSI in the respective national language(Chinese, Japanese or Korean) is compulsory for all participants in the ASBE programme and is supervised by several bilingually trained lecturers and native speakers. Active participation in the language course is compulsory and usually takes place during the lecture-free period before the summer semester. The costs are covered by the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics upon successful completion of the programme.
At the beginning of the course, a literature study is carried out with reference to the students' respective exchange countries. Based on the findings from the literature studies, students work in groups to create a podcast on current relevant topics in the Asian economic region. This encourages students to actively engage with social, political and economic issues and problems in the target countries. The course is rounded off with a workshop on intercultural skills development to familiarise students with the aspects of communication in different contexts. The models learned are then applied using so-called "critical incidents" experienced by previous participants in the ASBE programme.
An idea for the project work should also be developed during the preparation phase. Students independently find a professor to supervise them. A list of previous topics can be found at the bottom of this page.
To summarise, the preparation phase is based on the following four pillars:
- Fundamental linguistic and cultural competence
- Communicative and intercultural competence
- Professional competence
- Methodological competence
Please note that active participation in the courses is compulsory.
The stay abroad always takes place in the winter semester and represents the second phase of the programme. The focus here is on deepening Asian expertise through specialised modules at the partner university, project work and the use of the language learned in the country.
Specialised courses worth 20 ECTS* are taken during the stay abroad. A list of courses that have been offered in the past and the respective conversion into ECTS can be found at the bottom of this page.
In order to reflect on learning processes and personal experiences, a reflection diary should record the opportunities and problems experienced in order to identify differences between the cultures and adapt accordingly.
To summarise, the second phase is based on the following five pillars:
- Advanced linguistic and cultural competence
- Social competence
- Regional competence
- Professional competence
- Project competence
*Exchange studentsat Tohoku University have to take 35 ECTS due to a guideline of the partner university. Accordingly, the project work (ASBE 2) is replaced by two specialised courses with 5 ECTS each. In addition, a further 5 ECTS course must be taken, which can be credited outside the ASBE programme via the normal credit transfer system.
In the follow-up phase, students reflect on and evaluate their own findings. The project work is finalised in this phase and presented to fellow students, professors and the following ASBE year at a closing event. The final event is expected to take place in May.
In addition, the ASBE graduates will be available to the following year as contacts for questions and will organise a small country-specific workshop in the country groups to facilitate the exchange of experience and information between the years.
To summarise, the follow-up phase focuses on the following four pillars:
- Presentation skills
- Reflection skills
- social skills
- Project competence
Important notes
- Students at Tohoku University must take two specialised courses worth 5 ECTS credits each instead of the project work. This is due to a university policy of Tohoku University, which stipulates that exchange students must take courses worth a total of 35 ECTS.
- Management Master's students must take the ASBE 1 container module in the supplementary field instead of the Economics/VWL field.
- A container module cannot be split between two upper-division areas of your study plan. There must be 10 ECTS credits available for a container module in one upper-division area. Example: If you are taking two courses from the upper-division Business Administration module abroad and only have 5 ECTS credits available in the upper-division elective module and 5 ECTS credits in the upper-division Business Administration module, it is not possible to transfer credits. You need either 10 free ECTS credits in the upper-division elective module or the upper-division business/economics module.
- At Tongji University (Shanghai/China), students on the Master's degree programme in Business Education have the opportunity to complete business education credits in the VET track as part of their degree programme.
If you have any problems integrating the programme into your study plan, please contact the ASBE team during the application process.
Partner universities
Our network is large and consists of five universities in three different countries in Asia.
Application, financing and language courses
Applications can be submitted through the Paderborn University's central application procedure via the International Office in the winter semester prior to your stay abroad . Please note that only complete applications in accordance with the International Office's requirements can be considered.
You can apply if
- you are enrolled in a Master's programme of the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics at Paderborn University (all Master's programmes of the faculty can be found here) or
- you are at least in the 5th semester of a Bachelor's degree programme in the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics at Paderborn University and are enrolled in a Master's degree programme at the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics at UPB at the start of the programme.
Your letter of motivation for your application for a semester abroad should clearly state why you want to participate in the ASBE programme. No extra letter of motivation is required for the ASBE programme.
Further general information on the application for a semester abroad can be found here.
Due to the cooperation agreements, no tuition fees are generally charged at the partner universities.
The ASBE programme is based on the DAAD-ISAP framework project (International Study and Training Partnerships). Each partnership is assigned to its own ISAP project. Scholarship funding is therefore dependent on the chosen partner university. There are currently 5 scholarship places available for the partnerships with Beijing (Beijing Institute of Technology), Shanghai (Tongji University) and Seoul (EWHA University).
Country | Semester | Cities | Full scholarships for students | Travel allowances |
China | 01.09. - 31.01. | Beijing, Shanghai | 1.350 € 1.275 € | 825 € 825 € |
South Korea | 01.09. - 31.12. | Seoul | 1.275 € | 1.125€ |
The health insurance subsidy for German participants with a partial or graduate scholarship is generally €35 per participant per month. | ||||
Sources: DAAD funding rates depending on the respective project start date. You can find the funding rates for German students there.
For other universities, you can apply for scholarships such as PROMOS or from the Phoenix Contact Foundation independently of the ASBE programme. Further information can be found here.
In addition, the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics will cover the costs of the intensive language course lasting several weeks at the National Language Institute at the Ruhr University Bochum if you successfully complete the programme.
Language courses
The Faculty of Business Administration and Economics enables programme participants to take part in an intensive language course lasting several weeks in the respective national language at the National Language Institute at Ruhr University Bochum. Successful participation in the language courses is mandatory for participation in the ASBE programme. The course fee, corresponding teaching materials and the cheapest overnight accommodation will be covered if the ASBE programme is successfully completed.
| Language course | Course dates |
| Chinese I + II |
|
| Japanese I + II |
|
| Korean I + II |
|
Please note that the dates are subject to change. Please check the LSI website for any changes.
At the end of the language course, an oral examination will be conducted by the LSI. This is an individual assessment of your performance in the sense of a well-founded, competence-orientated examination. The performance achieved in the language course is recognised by Paderborn University to the extent of 5 ECTS. Based on their participation in class and the oral examination, participants receive a grade that counts 50% towards the overall grade for the ASBE I module (W4071). The examination fee of €30 is the responsibility of each participant and can be paid on site. Registration for the language course is collected by the ASBE programme management.
Courses offered at the partner universities

Please note that the courses offered by the partner universities may change each year. Courses that have been offered in the past can be a good guide, but are no guarantee that these courses will be offered again next year.
Ideally, you will receive a list of the current courses for the winter semester in question from the partner university.
Courses offered in previous years
English-language Master's courses can be attended at the School of Management and Economics, among others. The range of courses is constantly being updated. Frequently offered courses include: Intercultural Management (5 ECTS), Organisational Behavior (5 ECTS) and Research Colloquium (5 ECTS). You can also take a Chinese language course offered by the International Student Centre. Below you will find a selection of the courses available in WS 19/20.
- Intercultural Management
- Human Resource Management
- Managerial Economics
- Operation Management
- Strategic Management
- Business English
- Accounting
- Financial Management
- Management Accounting
- Employee Relationship Management
- Organisational Behaviour
Numerous English-language courses are offered at EWHA Womans University at the graduate/master's level: e.g. interdisciplinary courses from various faculties, subject-specific courses in the fields of business administration and economics from the Graduate School of International Studies (GSIS). All German exchange students are administratively supervised by the Office of International Affairs (OIA).
Here you will find the full range of courses offered by EWHA Womans University (for Master's students, please select "2nd semester" for winter semester under "Year/Semester"; for Graduate: "Graduate School of International Studies").
As part of the International Programme Oita University (IPOU), the University of Oita offers business courses in fields such as management, economics and economertrics. In addition to the elective courses, there are four compulsory Japanese language courses (Japanise 1: Grammar/Function, Conversation, Reading and Integrated Activities) and one compulsory course (Introduction to Japanese History, Culture and Society) in the field of culture.
Here you can find the courses offered by Oita University in the winter semester 2019/2020.
At Tohoku University, Master's courses of the International Programme in Economics and Management (IPEM) can be taken.
Here you can find a list of past courses: Master courses in English.
Our partner institute at Tongji University offers courses in vocational training and further education. Additional business, language and cultural courses can also be attended at other institutions of the university. This course programme changes from year to year.
Course programme 1: At the Chinese-German Institute for Vocational Education and Training (CDIBB), German exchange students have been able to choose between the following Master's-level specialist courses in recent years.
- Comparison of Chinese and German Vocational Education (compulsory)
- Newest Development of Vocational Education
- Governance and quality assurance of vocational education and training in Germany
- Qualification standards and aptitude tests for vocational school teachers in Germany
Course programme 2: International School
All German exchange students are administratively supervised by the Chinese-German University of Applied Sciences(CDHAW). A study-related introduction is provided on this page under "Students Guide".
VET-track: At Tongji University (Shanghai/China), students on the Master's degree programme in Business Education also have the opportunity to complete the VET-track, particularly in business education, as part of their degree programme.
Topics of completed project work
Topic |
Social Entrepreneurship in China |
A Risk Analysis of China's Financial System |
Does Culture Matter? How Cultural Differences between Asian and Non-Asian Hotel Guests Affect their Online Reviewing Behaviour |
Does Priming affect Performance? - An experimental approach |
International marketing with focus on China: Developing a successful Marketing Mic for Western companies operating in China |
Literature Review of International Management Concept/Theories used in the Chinese Context |
Retention Management in China - How is it implemented and which challenges does it face compared to Western countries? |
Corruption in China - Curse or blessing for German enterprises? |
The development and the possibilities of professional football in China from an economic point of view |
Voice behaviour of Chinese Employees |
Chinese as foreign language - Factors influencing the learning process |
Guanxi and Corruption - Analysis of the corruption scandal GlaxoSmithKline plc. using the principal-agent approach |
Entrepreneurship in China - An overview of the conditions in the emerging private sector |
China's Growth has its Price: Problems and Challenges after the Financial Integration |
Workaholism and Work Engagement - A Comparison between China and Germany |
Talent Management in China and Germany |
Aspects of diversity and diversity management in a multi-national-context |
The Hukou System: "An Impediment to inclusive growth in the People's Republic of China?" |
The study process questionnaire in relation to the Chinese Learner |
Shanghai vs. Hong Kong / Which City will have the Competitive Advantage and develop to be the Major Economic Centre in China? |
Corruption in China: Does Culture play a Role? |
Optimised Academic Learning Space:Features and Design Approaches (An Evaluation Study in Tongji University, Shanghai) |
Accounting in China: Historical Development and Current Status |
Two-sided markets: A qualitative analysis whether the China operating system can be defined as a two-sided market. |
Chinese Consumers' Perception of Domestic Automotive Brands Using the Example of Geely |
An empirical analysis using the Chinese brand Lenovo |
The influence of country of origin knowledge on consumers' brand perception - An empirical analysis using the Chinese brand Lenovo |
A closer look at Chinese working women |
Intellectual Property Infringement in China. Implications of Piracy and Counterfeiting and its Contribution to Development |
Arthur Lewis's Growth Model and China's Industrial Development |
The influence of institutional quality on international acquisition performance with a focus on China |
The Chinese Banking System - An approach to measure the fragitlity of the Chinese Banking System |
Organisation and Development of Study Programs - A Case Study of the Chinese Higher Education Systems |
Challenges and Problems in the Implementation Process of the German Dual System of Vocational Education and Training in China to Overcome the Worker Skilled Shortage |
Mobility in Beijing compared to Berlin: How is electric mobility performing in local business models? - Comparing to established alternatives? - Actual situation and forecast. |
Strategic and financial analysis of China Souther Airlines - Particularities of the Chinese civil aviation sector |
Topic |
Comparison of blockchain technology acceptance between Germany and South Korea |
"Mittelstand" and "Jaebeol" - Impact on Innovation |
The Korean Innovation Model - Is Korea able to take the leader position in eco-innovation? |
Korean Women in Leadership Positions |
South Korea - Economic Wonderland: Chaebol as Support or Obstacle for the Korean Success |
How Gendered Wording and Pictures in Job Advertisements Influence Student's Interest in a Vacant Position - A Study in South Korea |
The Influence of Individualism versus Collectivism on Entrepreneurship and its Effect on Economic Growth |
Job recruiting procedures across cultures |
Occupational gender segregation in Korean labour market |
Employer branding as a recruiting measure and generation of employee attraction? |
International Competitiveness due to economic policies? An inside look at the paragon South Korea |
Civic Engagement in Higher Education: Theory and Practices in South Korea |
Business and Human Resource Education & Higher Education |
The historical development and current importance of the Chaebol industry for the South Korean economy |
Securing access to key energy and mineral resources - A South Korean perspective on the global challenge |
Stereotypes and their impact in job advertisements: The Case of South Korea |
Blowing the Whistle in South Korea - How Asian Values influence Whistleblowing |
The Japanese Labour Market -Implications on marriage decisions and the employment of women |
The Seismic Hazard - The Impact on the Japanese Real Estate Market |
The impact of Computerization in Japan: Does Digitisation and Automation transpire differently due to cultural issues? |
Is an eased immigration policy a chance to encounter the economic consequences of the aging population in Japan? |
Labour Market Dualism in Japan |
Cultural Impact in the Sharing Economy - An Empirical Cross-Cultural Study |
Japanese Women in Management and the prospects for gender equality in Japanese companies |
Karōshi (過労死) Death through Overwork in Japan |
The Great East Japan Earthquake - Economic impacts on Japan |
Can suitable Disaster Management pose an Opportunity for Economic Growth in the Construction industry? Miyagi and the Tohoku Earthquake - A Look beyond the Damages |
Abenomics - A gamble for a brighter future of Japan? |
The influence of institutional relationships, financial systems, and banking systems on economic stability in the United States and Japan in the face of economic crises |
How Important Is Population Ageing For The Promotion Of Robotics: The Case Of Japan |
The Influence of Egalitarianism on International Joint Venture |
Job recruiting procedures across cultures |
The lost decades of Japan - A structural phenomenon of developed countries? |
Corruption in Japan with focus on the Yakuza: How enrooted is corruption in Japan and to what extent does the crime organisation contribute? |
Japanese debt - International comparison and sustainable development |
Economic Transformation and Cultural Change - the Case of Japan |
Workaholism and Work Engagement in |
Competitive Strategies in Oligopolistic Markets |
How do we interpret random biased effected results? An experimental study at the University of Oita in Japan |
Implications of Supply Chain Management in Keiretsu for German Enterprises |
Abenomics: a possible way to overcome the Japanese Stagnation |
The influences of demographic change on the Japanese economy |
Women in the Japanese Labour Market |
The acceptance and use of robots in service situations in Japan |
Modelling Stock Returns of Several Japanese Companies Using the Semi-APARCH Model |
Influences of Cultural Response Patterns on Cross-National Research with Reference to Japan |
Contact and FAQ
If you have any questions about the program, you are welcome to come to our open office hours or contact us via e-mail.
Office Hours (October & November)
- Tuesdays, 2–3 PM: Open Office Hours in Room Q1.431
- Thursdays, 2–3 PM: Online Office Hours (MS Teams)
Alternative appointments can be arranged by email.
In this section we have compiled useful links and information about the ASBE programme. You can gain a good impression of the ASBE programme from experience reports, interviews and completed projects.
FAQ
Do I have to attend a language course? | Yes, full and successful participation in the language courses already scheduled by the LSI in Bochum is compulsory. You can view the scheduled dates in the Language Courses field above or directly on the LSI website. |
Can I also learn the course content independently at home and only come to the language centre in Bochum for the exam? | No, this is not possible. Attendance at the language course is compulsory. |
I already have language skills in Korean/Japanese/Chinese, do I still have to attend the language course? | Participation in the language course is also compulsory in this case; if you already have previous knowledge of the respective target language, please contact the ASBE team. |
How is the language course financed? | Participation in the course and accommodation at the LSI in Bochum is financed by the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics - participants pay the examination fees themselves. |
How many ECTS must I keep free for the ASBE programme? | A total of 40 grade-relevant ECTS must be kept free in the study plan for the modules to be completed for the ASBE programme. These are made up of four 10 ETCS modules ASBE I to IV ("container modules"). In a nutshell, it is expected that the credits earned abroad as part of the ASBE II to IV modules - as far as possible - match the subject matter of your Master's programme - this must be taken into account when choosing the topic of your project work (ASBE II) and the course selection at the target university (ASBE III and IV). Please note that the field of method modules is not available for credit transfer abroad. |
Unfortunately, I only have 30 grade-relevant ECTS credits left in my study plan, can I book an ASBE module as an additional module in my credit account? | No, this option is generally not available. 40 ECTS must be kept free in the grade-relevant field. Please note that the field of method modules is not available as a credit transfer area for credits earned abroad (see above). |
Are scholarships available for all partner universities? | You can find the current scholarship-funded cooperations in the table above. Please note that special situations such as the Corona crisis may affect the availability of scholarships. Any adjustments to the funding of scholarships are decided by the scholarship provider and cannot be influenced by the ASBE team. |
Can I receive other scholarships - i.e. a second scholarship - in addition to the ASBE scholarship? | The funding guidelines prohibit some secondary scholarships. However, in other cases it is also generally not advisable to claim further scholarships, as these are usually credited in full or the ASBE scholarship is reduced accordingly. You must notify us if you wish to claim a second scholarship. |
Can I receive BAföG funding in addition to the ASBE scholarship? | Yes, this is possible. However, this will also be taken into account in full or the ASBE scholarship will be reduced accordingly, so that additional funding is generally not recommended and primarily means additional administrative work. It is mandatory that you notify us of any BAföG funding you are claiming (see above). |
Where can I find the module catalogue of the partner university? | You can find examples of past courses above. Please note, however, that the course catalogue may change from time to time. |
Is there an ECTS conversion table so that I know how many ECTS are recognised for a course abroad? | Grade conversion tables can be found here. |







